



The project is done by Simon (01-02) and David (01-02).
![]() Index:
Index:
1.
History
2.
The Structure Of Plastic
3.
Usage
4.
Importance
5.
How To Made Plastic
6.
The Coloring of plastic
7.
The Structure Of Plastic
8.
Introduce Some Plastic
9.
 Environment
Environment
10.
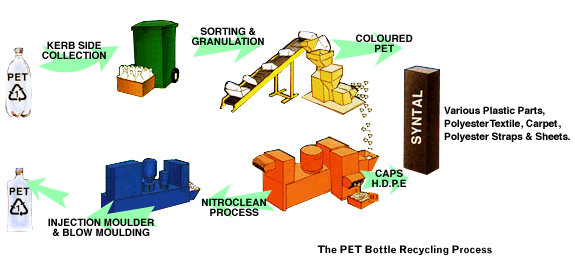
Recycling
11.
The Future Of Plastic
12.
Interest Thing Form This Project
The History Of Plastic:
The first man-made plastic was created by Alexander
Parkes who first publically demonstrated it at the 1862 Great International
Exhibition in London. The material called Parkesine was an organic material
derived from cellulose that once heated could be molded and retained its shape
when cooled.
With the start of the 1930’s came the
‘Poly’ era:
The German chemist Eugen Baumann first created PVC in 1872. However it was
never patented until 1913. Inventor, Friedrich Heinrich August Klatte initiated
the polymerization of vinyl chloride with sunlight. Klatte was the first
person to receive a patent for PVC
At about the same time an American producer, Du Pont, launched the first
polyamide —nylon 66 — perfected after minute analysis of the structure of silk
by their chemist Wallace Carothers. Nylon is a synthetic thermoplastic material
introduced in 1938. It is strong elastic, resistant to abrasion and chemicals
and low in moisture absorbency.
The major event in the UK came in 1935 when, after three years research, ICI
Alkali Division laboratories produced polyethylene.
Another material with a lengthy gestation was polystyrene. Originally
discovered in 1939 by a German apothecary Simon, it was another German, organic
chemist Staudinger, who realized that the solid that Simon had isolated from
natural resin was in fact composed of long chains of styrene molecules.
Perspex first produced commercially in the UK in 1934.
The Usage Of Plastic:
In this century, we use a lot of plastic. Let me introduce something to us.
 Plastic Bag
Plastic Bag
 Food container.
Food container.
 Drink Container
Drink Container
 Domestic
Product
Domestic
Product
The
Importance Of Plastic
The plastic become an importance industry in the world. It
replace metal because it has different properties, some of them are flexible,
some of them are transparent, some of them are transparent, some of them are
strong.
It doesn’t corrode and rust. It is cheap. It is resistant to chemicals. This
advantage make the plastic become a important role in the world.
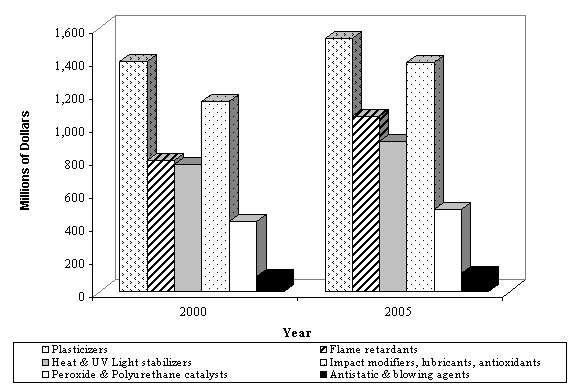
U.S.A Market for Major Plastics Additives,
through 2005
The
Importance Of Economic
As the material plastic has helped improve
the quality of our lives, the plastics industry has become an increasingly
significant contributor to the United States economy. Indeed, in 1996 the
plastics industry accounted for more than 1.3 million jobs and $274.5 billion
in shipments. The United States is the largest consumer and producer of
plastics in the world, a role that goes along with having the world's largest
economy, some of the least expensive chemical feedstock’s, and an excellent
petrochemical infrastructure. Below is more detailed information about the role
of the plastics industry on the U.S. economy.
|
Growth of Plastics Industry Jobs |
|
|
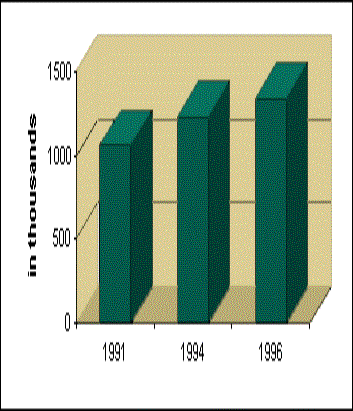
Employment
Employment
in the plastics industry has increased steadily in the past two and a half
decades, growing at an annual rate of 3%. This steady rise in employment is in
sharp contrast to overall manufacturing employment, which decreased by an
average annual rate of 0.3% over the same time period. Over 1.3 million U.S.
workers were directly employed by the plastics industry in 1996. This means that
11.3 out of every 1,000 nonagricultural workers is employed by the plastics
industry. If upstream, supplying industries (industries that provide
feedstocks, spare parts and other related services) are included, the number of
plastics industry employees rises to 2.3 million. This figure represents nearly
2% of the entire U.S. workforce.,
|
Growth of Plastics Industry Shipments |
|
|
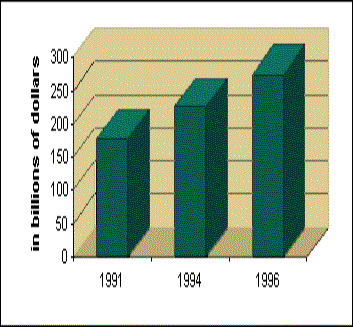
Shipments
Like employment, the value of shipments of plastics has grown at an impressive rate in the last two and a half decades. U.S. shipments of plastics (shipments directly generated by producers of plastics raw materials, product manufacturers, machinery companies, moldmakers, wholesale distributors and plastics processors) totaled $274.5 billion in 1996. This figure represents an increase of 55% since 1991. On average, plastics industry shipments have increased by an annual rate of 4.1% since 1974. This is in contrast to the overall manufacturing industry, which grew by an average annual rate of only 1.3 % over the same period. Including upstream, supplier industries, shipments totaled $366.4 billion in 1996, ranking the plastics industry fourth among top manufacturing industry groups, behind only motor vehicles, petroleum refining, and eletronic components and accessories.
This show that the plastic is not only
affected our living quality, it also make a lot of job for the people
How
To Made Plastic
Thermoplastics
1.
Heat
the solid thermoplastic
2.
Liquid
thermoplastic poured into mould
Or
1.
Put
the raw plastic material into the mounding machine
2.
The
plastic is melted and injected into a mould.

Thermosetting
plastics
1.
A
powered mixture, which contains the plastic and a dye, is placed in the lower
half of a mould that is then heated.
2.
As
the powder softens, the upper half of the mould is lowered to compress the
plastic into shape.
How To Make Plastic
Thermoplastics/Thermo softening plastics
1.
Heat the
solid thermoplastic
2. Liquid thermoplastic poured into mould
OR
Put the raw plastic material into the moulding machine
The plastic is melted and injected into a mould.

Plastic Injection Moulding machines ranging from
20-1,250 tonnages


Automated Moulding The model shown
here is 220 tonnage injection machine
Thermosetting plastics
1.
A powered
mixture, which contain the plastic and a dye is placed in the lower half of a
mould that is then heated.
2.
As the powder softens, the upper half
of the mould is lowered to compress the plastic into shape.